Fuel tank monitoring
Remote monitoring system for truck tankers
Applications
Many vehicle telematics and stationary object monitoring systems provide fuel tank monitoring feature. Quite often, fuel level measurement is one of the core fleet’s requirements to GPS vehicle tracking system for trucks, construction and agricultural equipment.
Moreover, information on fuel volume fill ups and fuel draining volumes from tank or storage is useful for telematics systems of vessels and railroad machinery – equipment with high fuel consumption. Increasingly, fuel level measurement and remote monitoring is implemented for diesel power generator sets, heating equipment rooms and corporate gas stations.
Fuel tank monitoring allows fleet manager or machinery supervisor to:
Measure precise volumes of fuel tank refill
Detect fuel siphoning from fuel tank
Prevent fuel theft from tank (e.g. underfilling or siphoning)
Reveal fuel mixing with extraneous liquids (e.g. waste oil);
Compare fuel quality of different suppliers/gas stations
Indirectly define fuel consumption
Schedule supply tank refill of stationary engine
Benefits of implementing fuel tank monitoring
Higher transparency of fuel costs accounting – fuel level monitoring helps fleets to determine precise volumes and exact places of fuel tank refilling, combining that information with fuel bills.
Eliminated fuel theft from tank – fuel volume measurement allows detecting date, time and volume of fuel siphoning and helps to prevent unwanted attempts of fuel drain in future.
Extended lifetime of fuel system and lower maintenance costs – mixing high-quality fuel with extraneous liquids (water, alcohol, used engine oil) leads to early engine breakdown and high costs for repair. That can be eliminated by detecting and alerting fuel quality change, what can be done by fuel monitoring system.
Increased fuel economy and optimized fuel cost – indirect “measurement” of fuel use (i.e. by decrease of fuel level in tank), preventing theft from fuel tank, excluding fraud attempts with sales slips – all that helps fleets to implement fuel economy measures, and thus reduce company’s fuel expense.
Easier trip reporting and transfer of vehicle between drivers – less time spent for after-trip reporting by driver and quicker transfer of vehicle between drivers (e.g. shifts) increases overall performance of fleet. Also, automated fuel level measurement allows easier fuel data integration into ERP and accounting platforms.
Ways of fuel tank monitoring
A. Install additional sensor in fuel tank
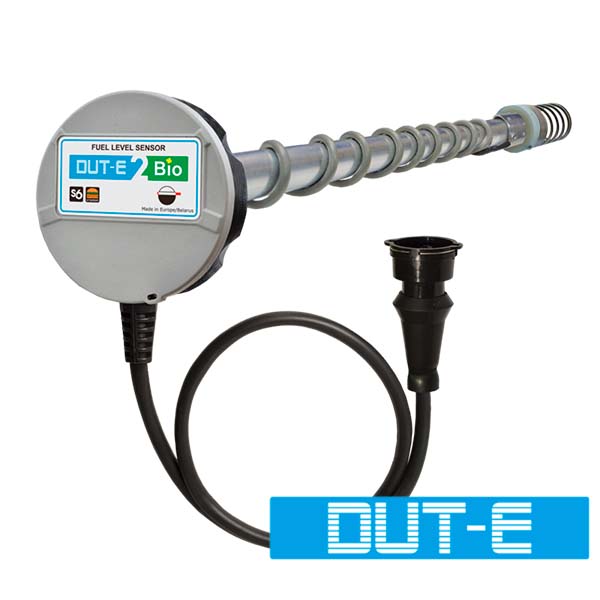
There are many types of additional sensors for fuel volume measurement – ultrasonic, hydrostatic, reed-switch, capacitive with a string, capacitive with rod, capacitive with coaxial pipes. Each type has its own advantages. Wagencontrol is a manufacturer of capacitive fuel level sensors with coaxial pipes – DUT-E. The main advantages of fuel level sensors by Wagencontrol is simplicity of probe design – no movable parts, easy probe cutting and length extension, large measuring area comparing to other types of capacitance sensors (that provides higher resolution capability i.e. higher sensitivity of detecting fuel level change). The fuel sensor sends fuel level, fuel volume, fuel temperature, ambient temperature, fuel type and 40 other parameters.
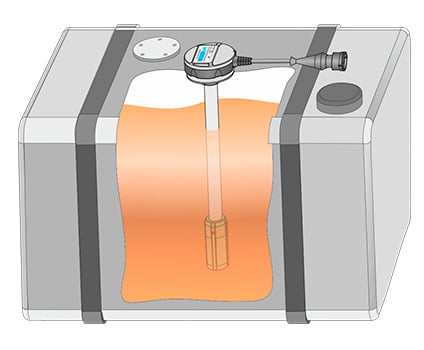
Example of DUT-E installation
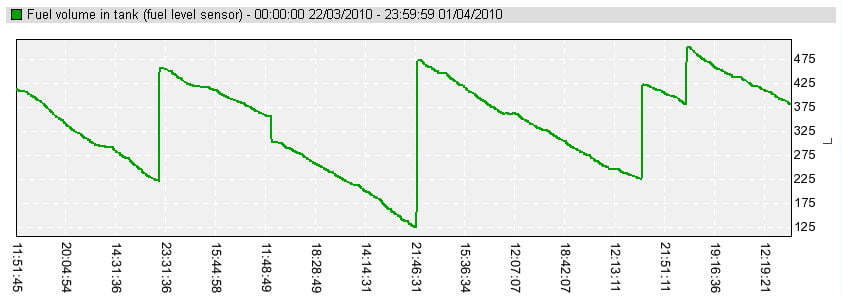
Advantages of additional fuel level sensor
High accuracy of level measurement
High sensitivity to level change
No blind areas over the entire height of fuel tank
Suitable for almost all types of fuel tanks
Can be used for old vehicles without ECU and CAN bus
Readings are independent on ambient temperature
Automatic conversion of level (mm) to volume (liters)
Detects fuel type change (differential fuel level sensor)
Independent power supply (wireless BLE fuel level sensor)
Disadvantages
Takes time to be installed, installation technician should have necessary skills
Should be configured and connected to a proper GPS tracking device or telematics gateway
Installation costs are higher comparing to CAN bus data reading
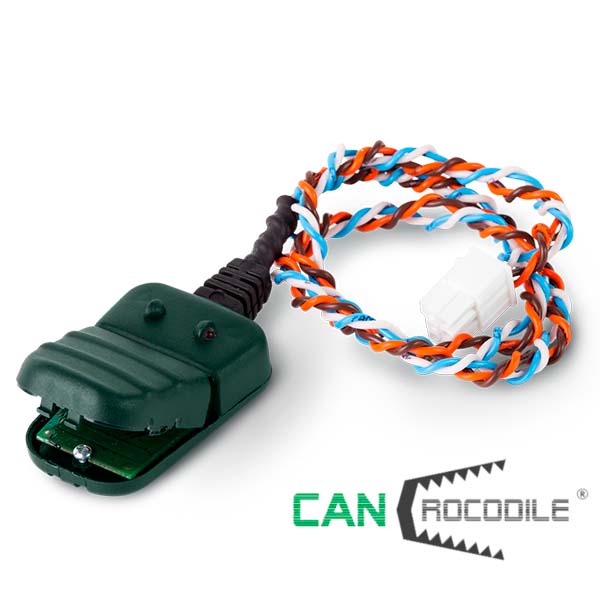
B. Fuel level data from CAN J1939 bus
The easiest way to monitor fuel level, that can be used for engines with electronic control unit (ECU). Data on fuel level is received from CAN J1939 bus, where it comes from standard fuel level sensor of a vehicle/equipment. Standard sensors have lower accuracy comparing to additional FLS because standard sensor are not initially designed for accurate fuel tank monitoring. Also, connection to CAN bus should be done cautiously without interference to ECU operation – special CAN bus readers can be used for that.
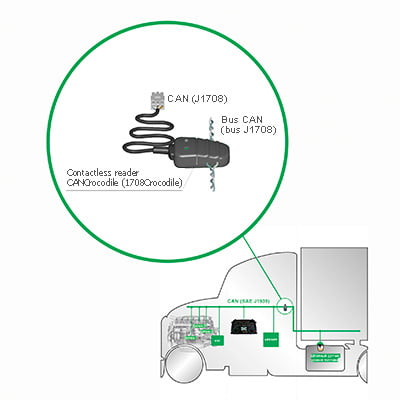
Example of CAN bus reader installation
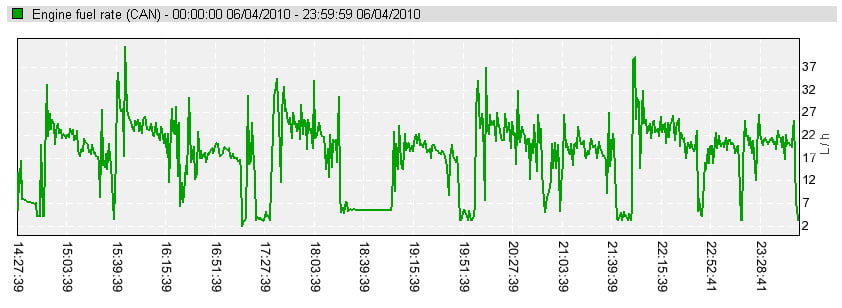
Disadvantages
Not suitable for old equipment, which has no ECU and CAN bus
Some vehicles might have corrupted, missing or encrypted messages on J1939 bus
Accuracy is usually lower. To obtain higher accuracy, tank calibration is needed.
Fuel level readings are dependent on temperature (false alarms might occur)
Some standard sensors have blind areas in the upper and lower part of fuel tank
No “level to volume” linearity – critical for non-rectangular shaped fuel tanks
Advantages of fuel tank monitoring using CAN J1939 data
Low cost of data reading equipment
Easy connection to CANbus and/or J1708 bus
Quicker installation of fuel monitoring system
Possibility to get other FMS parameters (RPM, oil pressure etc.)
Usage cases
Construction company (Qatar)
Task: fuel tank monitoring, GPS vehicle tracking.
Solution:
DUT-E GSM fuel level sensor with built in GPS and GSM modules.
Vic Florido, entrepreneur (Philippines)
Task: fuel theft prevention on road building machinery.
Solution: DUT-E GSM fuel level sensor.
Starcom Systems, Israel
Task: fuel level measurement in cisterns of truck tankers.
Solution: DUT-E 2Bio differential fuel level sensors








