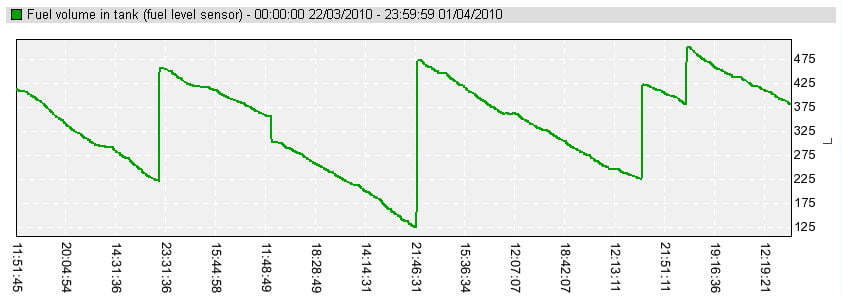
Using fuel level gauge indicator position on dashboard for determining how much fuel is left in a tank is not definitely the most accurate way. Since the indicator is not intended for showing fuel volume precisely, it only allows driver to understand approximate residues in tank – full, half, quarter etc.
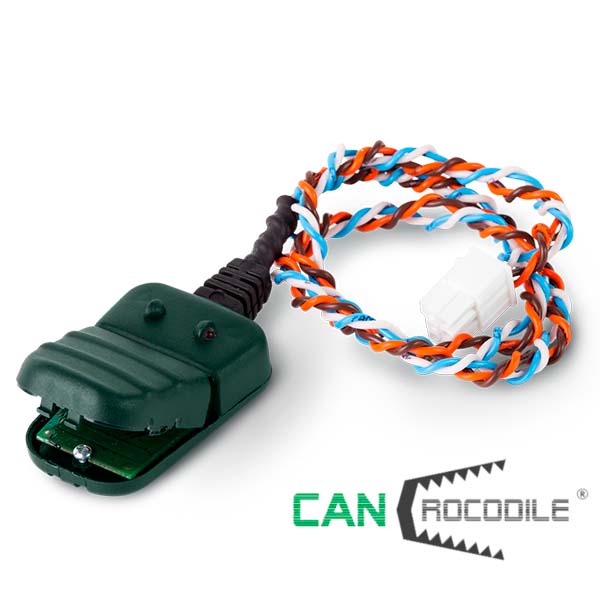
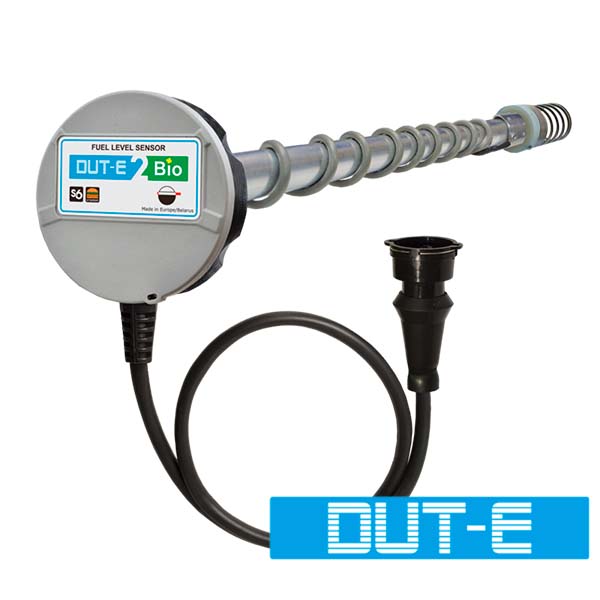
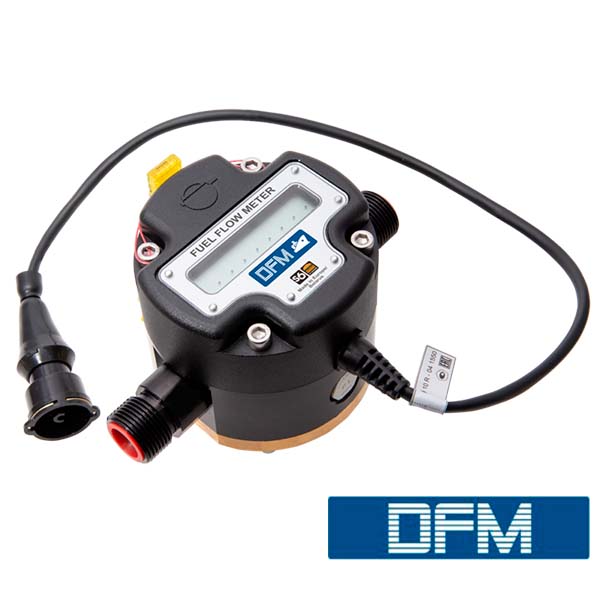
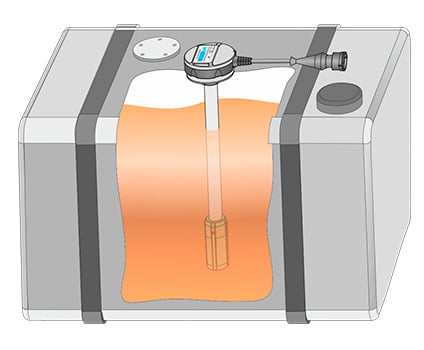
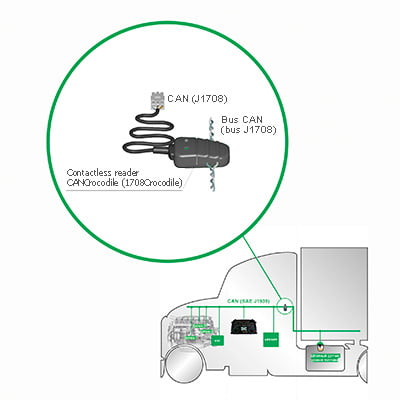
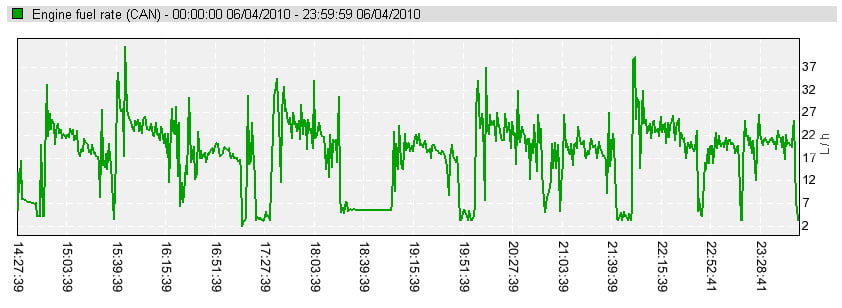
To get accurate data on remaining fuel, volumes of fuel tank fill up and potential manipulations with fuel, fleets usually rely on automated fuel tank monitoring. There are two main ways how to integrate fuel tank data into telematics system – measure fuel level by special additional sensor or read fuel level data from automotive CAN bus.